A free body diagram (FBD) is a graphical representation used in physics and engineering to visualize the forces acting on a single object. By isolating the object from its surroundings and representing all external forces as vectors, FBDs provide a powerful tool for applying Newton's laws of motion:
Each force vector is drawn with:
The key principle is to include only forces acting ON the object, never forces exerted BY the object on other entities.
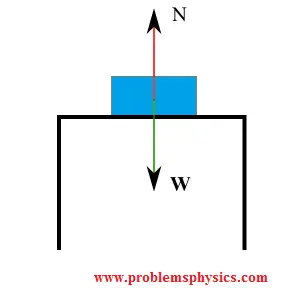
Forces acting on the stationary book:
Since the book is in equilibrium (\( \vec{a} = 0 \)), Newton's First Law gives: \[ \sum F_y = N - W = 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad N = W = mg \] The horizontal forces sum to zero trivially.
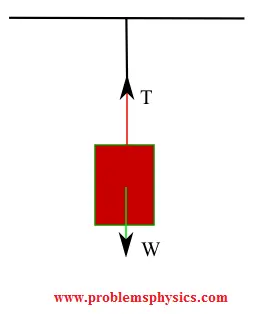
Forces on the stationary suspended block:
Equilibrium condition yields: \[ \sum F_y = T - W = 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad T = W = mg \] The tension force arises from the rope's molecular bonds resisting stretching.
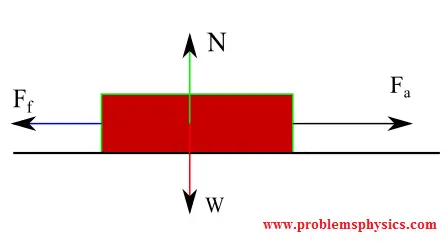
Forces acting on the block (assuming motion or impending motion):
The friction magnitude is given by \( f_f = \mu_k N \), where \( \mu_k \) is the kinetic friction coefficient. Vertical equilibrium gives \( N = W \). Horizontally: \[ \sum F_x = F_a - f_f = ma_x \] where \( a_x \) is the block's acceleration.
Forces on the falling object:
Applying Newton's Second Law: \[ \sum F_y = W = mg = ma \quad \Rightarrow \quad a = g \] The object accelerates downward with gravitational acceleration \( g \approx 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
Forces acting on the box:
Resolving weight into components: \[ W_{\parallel} = mg\sin\theta \quad \text{(down the incline)} \] \[ W_{\perp} = mg\cos\theta \quad \text{(into the incline)} \] Since there's no friction, the net force along the incline is \( mg\sin\theta \), causing acceleration: \[ a = g\sin\theta \] Perpendicular to the incline: \( N = mg\cos\theta \).

Forces on the box:
If the box is stationary, friction adjusts to satisfy equilibrium: \[ \sum F_{\parallel} = F_a + f_s - mg\sin\theta = 0 \] \[ \sum F_{\perp} = N - mg\cos\theta = 0 \] The maximum static friction is \( f_{s,\text{max}} = \mu_s N \), where \( \mu_s \) is the static friction coefficient.

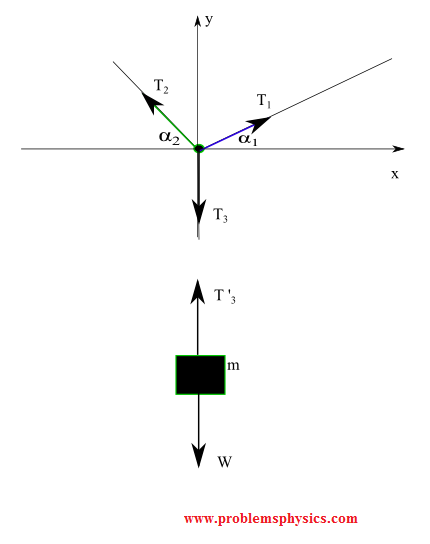
A) Free body diagram for the block (two forces):
Vertical equilibrium: \( T_3' = W \).
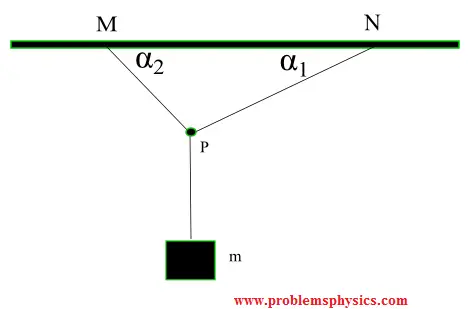
B) Free body diagram for junction point P (three forces):
The junction is in equilibrium: \[ \sum F_x = T_{2,x} - T_{1,x} = 0 \] \[ \sum F_y = T_{1,y} + T_{2,y} - T_3 = 0 \] where \( T_3 = W \). This system solves for \( T_1 \) and \( T_2 \) given the angles.

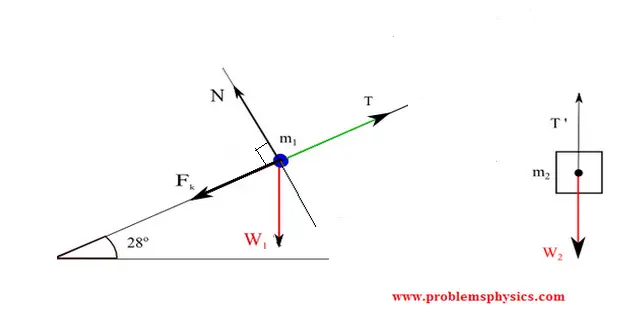
A) Free body diagram for block \( m_1 \) on incline:
Along the incline (x-direction): \[ \sum F_x = T - f_f - m_1g\sin\theta = m_1a \] Perpendicular to incline: \( N = m_1g\cos\theta \), with \( f_f = \mu_k N \).
B) Free body diagram for hanging block \( m_2 \):
Vertical equation: \[ \sum F_y = m_2g - T' = m_2a \] assuming downward is positive for \( m_2 \). The two equations combine to solve for acceleration \( a \) and tension \( T \).