Examples with explanations on the concepts of average speed and average velocity of moving objects. More problems and their solutions can be found on this website.
The average speed is a scalar quantity (magnitude) that describes the rate of change of the distance traveled by a moving object with respect to time.
\[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{\text{Total distance}}{\text{Total time}} \]
The average velocity is a vector quantity (magnitude and direction) that describes the rate of change of the position of a moving object with respect to time.
\[ \text{Average velocity} = \frac{\text{Change in position}}{\text{Time}} = \frac{\text{Displacement}}{\text{Time}} \]
An object moves from A to D along the red path as shown below in 41 minutes and 40 seconds.
a) Find the average speed of the object in m/s.
b) Find the average velocity of the object in m/s.

Solution:
a) Using the given scale (1 km per division), the total distance \(d\) is: \[ d = AB + BC + CD = 2 + 5 + 2 = 9 \text{ km} \] Total time: \(41 \text{ min} + 40 \text{ s} = 2500 \text{ s}\) \[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{9000 \text{ m}}{2500 \text{ s}} = 3.6 \text{ m/s} \]
b) The displacement is the vector from A to D with magnitude 5 km east. \[ \text{Average velocity} = \frac{5000 \text{ m}}{2500 \text{ s}} = 2.5 \text{ m/s (east)} \]
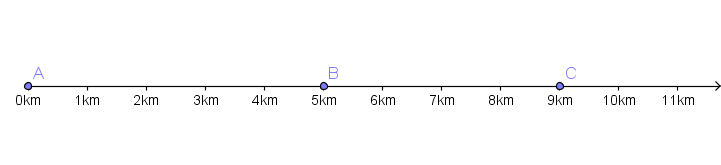
An object moves, along a line, from point A to B to C and then back to B again as shown below in half an hour.
a) Find the average speed in km/h.
b) Find the magnitude of the average velocity in km/h.
Solution:
a) Total distance: \[ d = AB + BC + CB = 5 + 4 + 4 = 13 \text{ km} \] \[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{13 \text{ km}}{0.5 \text{ h}} = 26 \text{ km/h} \]
b) Displacement from initial A to final B is 5 km. \[ \text{Average velocity} = \frac{5 \text{ km}}{0.5 \text{ h}} = 10 \text{ km/h} \]
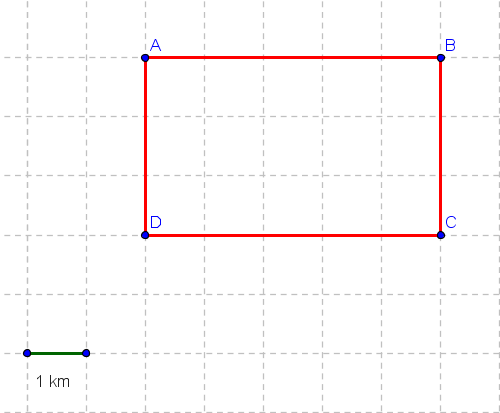
An object moves from point A to B to C to D and then back to A along the rectangle shown below in 5 seconds.
a) Find the average speed in m/s.
b) Find the average velocity in m/s.
Solution:
a) Perimeter: \[ d = 2(AB + BC) = 2(5 + 3) = 16 \text{ km} \] \[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{16000 \text{ m}}{5 \text{ s}} = 3200 \text{ m/s} \]
b) The object returns to the starting point, so displacement = 0. \[ \text{Average velocity} = 0 \text{ m/s} \]
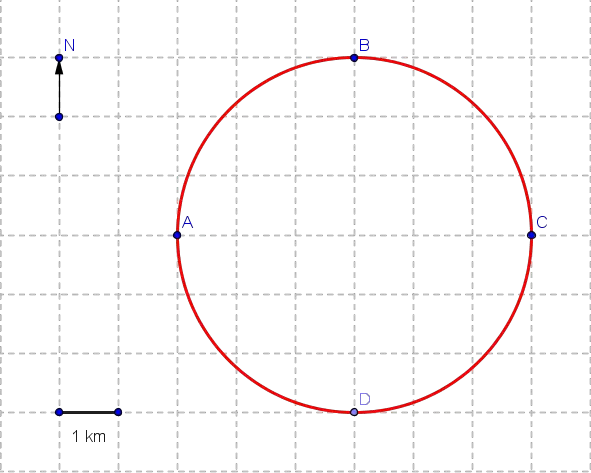
A person walks for two hours from point A to B to C along a circular field as shown below.
a) Find the average speed in km/h.
b) Find the average velocity.
Solution:
a) Distance is half the circumference: \[ d = \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = 3\pi \text{ km} \] \[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{3\pi \text{ km}}{2 \text{ h}} \approx 4.71 \text{ km/h} \]
b) Displacement is the diameter AC (6 km east): \[ \text{Average velocity} = \frac{6 \text{ km}}{2 \text{ h}} = 3 \text{ km/h (east)} \]
A person walks for one hour and 12 minutes from point A to B along a circular field as shown.
a) Find the average speed in km/h.
b) Find the magnitude of the average velocity in km/h.

Solution:
a) Distance is quarter circumference: \[ d = \frac{1}{4} \times 2\pi r = 1.5\pi \text{ km} \] Time: \(1.2 \text{ h}\) \[ \text{Average speed} = \frac{1.5\pi \text{ km}}{1.2 \text{ h}} \approx 3.93 \text{ km/h} \]
b) Displacement is chord AB. Using Pythagorean theorem: \[ AB = \sqrt{3^2 + 3^2} = 3\sqrt{2} \text{ km} \] \[ \text{Average velocity} = \frac{3\sqrt{2} \text{ km}}{1.2 \text{ h}} \approx 3.54 \text{ km/h} \]