Refraction of Light Rays in Different Situations
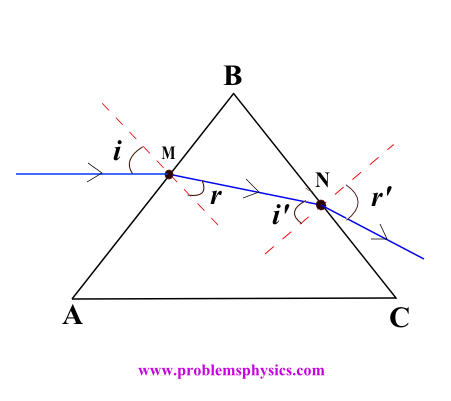
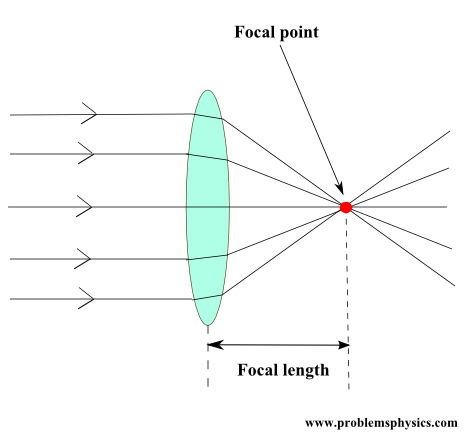
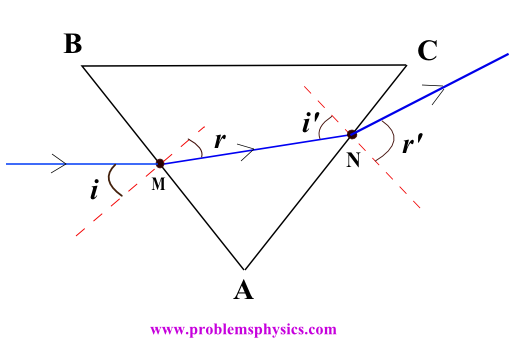
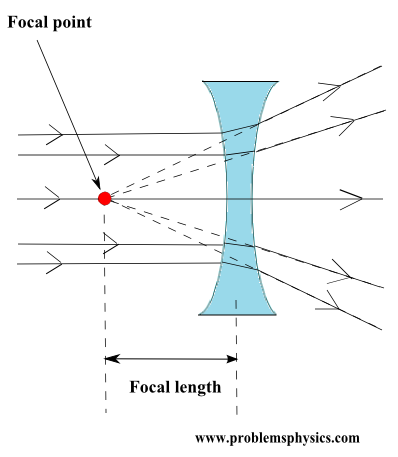
Understanding refraction is essential for studying convex and concave lenses. We examine the angle of deviation when light passes from a medium with refractive index \(n_1\) to one with \(n_2\).
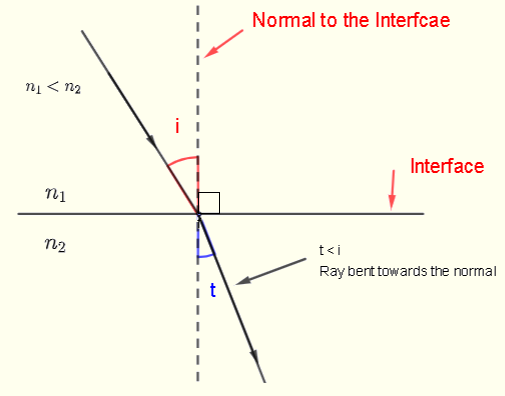
Case 1: \(n_1 < n_2\)
Snell's Law states:
Since \(n_1/n_2 < 1\), we have:
The refracted ray bends toward the normal when entering a more optically dense medium.
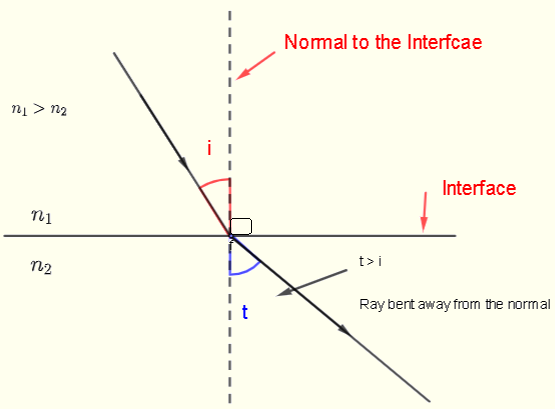
Case 2: \(n_1 > n_2\)
From Snell's Law with \(n_1/n_2 > 1\):
The refracted ray bends away from the normal when entering a less dense medium.
Case 3: Normal Incidence (\(i = 0\))
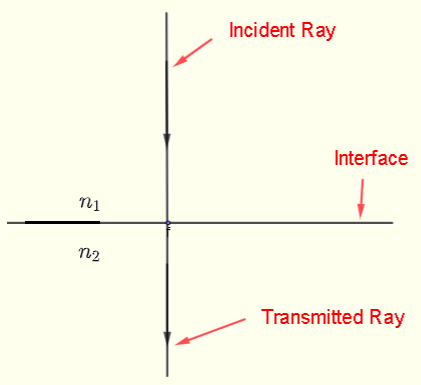
The ray transmits without deviation.
Example 1
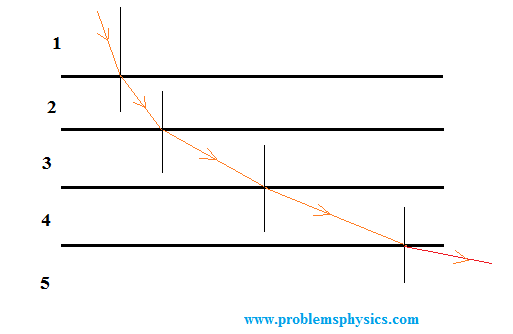
A light ray passes through five media with increasing refraction angles.
a) Which medium has the lowest refractive index?
b) Which medium has the lowest speed of light?
Solution
a) Increasing refraction angles indicate decreasing refractive indices. Medium 5 has the lowest \(n\).
b) The speed in a medium is \(v = c/n\). Medium 1 has the highest \(n\), thus the lowest \(v\).