Optics Questions with Solutions
Practice optics questions with detailed solutions and explanations. These problems are designed to help prepare for the SAT Physics test. Topics include
reflection,
refraction,
critical angle,
lenses, optical fibers, and refractive index.
-
Which of the following is true about light?
I) It is an electromagnetic wave
II) It does not propagate in vacuum
III) Its maximum speed is approximately \(3 \times 10^8 \, \text{m/s}\)
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) III only
E) I, II and III
-
The speed of light in a certain material is 50% of its speed in vacuum. What is the refractive index of this material?
A) 1.5
B) 0.5
C) 6.0
D) 2.0
E) \(1.5 \times 10^8\)
-
What is the critical angle \(i_c\) at the glass-cladding interface of an optical fiber with core refractive index \(n_1 = 1.5\) and cladding refractive index \(n_2 = 1.45\)?
A) \(15^\circ\)
B) \(105^\circ\)
C) \(86^\circ\)
D) \(83^\circ\)
E) \(75^\circ\)
-
Which of the following is true about monochromatic light?
I) It can be refracted
II) It cannot be dispersed
III) It can be reflected
A) I, II and III
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) I and III only
E) None
-
A light ray travels from medium 1 (speed \(s_1\)) to medium 2 (speed \(s_2\)). If \(s_1 > s_2\), then at the interface:
A) The ray refracts away from the normal
B) The ray refracts toward the normal
C) The ray follows a straight path
D) The angle of reflection is greater than the angle of incidence
E) The angle of reflection is not equal to the angle of incidence
-
Parallel rays strike a convex lens. Which diagram shows the correct ray behavior?
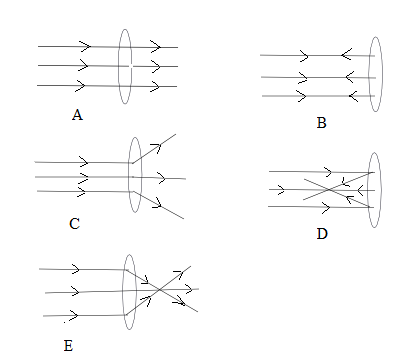
-
A 10 cm tall object is placed 50 cm in front of a biconvex lens with focal length 20 cm. Which is true about the image?
I) The image is virtual
II) The image is on the opposite side from the object
III) The image is inverted
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) II only
E) III only
-
A 5 cm tall object is placed 25 cm in front of a biconvex lens with focal length 10 cm. What is the image height?
A) 2.5 cm
B) 12.5 cm
C) 6.8 cm
D) 3.4 cm
E) 7.4 cm
-
An optical fiber has core index \(n_1 = 1.6\) and cladding index \(n_2 = 1.5\). What is the maximum angle \(\alpha\) that light rays can make with the fiber axis to maintain total internal reflection?
A) \(10^\circ\)
B) \(15^\circ\)
C) \(20^\circ\)
D) \(70^\circ\)
E) \(90^\circ\)
-
For an object in front of a plane mirror, which statements about the image are true?
I) The image is real
II) The image is upright
III) The image height is twice the object height
A) I, II and III
B) I and II only
C) II only
D) I and III only
E) None
Solutions
-
Light is an electromagnetic wave that propagates in vacuum at approximately \(3 \times 10^8 \, \text{m/s}\).
Answer: C
-
\(v = 0.5c\)
Refractive index: \(n = \frac{c}{v} = \frac{c}{0.5c} = 2\)
Answer: D
-
Critical angle: \(i_c = \arcsin\left(\frac{n_2}{n_1}\right) = \arcsin\left(\frac{1.45}{1.5}\right) \approx 75^\circ\)
Answer: E
-
Monochromatic light can be reflected and refracted but not dispersed.
Answer: A
-
Using Snell's Law: \(n_1 \sin i = n_2 \sin r\)
Since \(n = \frac{c}{s}\), we have \(\frac{\sin r}{\sin i} = \frac{s_2}{s_1} < 1\), so \(r < i\). The ray bends toward the normal.
Answer: B
-
A convex lens converges parallel rays to the focal point.
Answer: E
-
Using the lens equation: \(\frac{1}{d_o} + \frac{1}{d_i} = \frac{1}{f}\)
\(\frac{1}{50} + \frac{1}{d_i} = \frac{1}{20}\)
\(d_i = 33 \, \text{cm} > 0\) → real, inverted, opposite side.
Answer: C
-
Lens equation: \(\frac{1}{25} + \frac{1}{d_i} = \frac{1}{10}\) → \(d_i = 17 \, \text{cm}\)
Magnification: \(m = \frac{h_i}{h_o} = -\frac{d_i}{d_o} = -\frac{17}{25}\)
\(h_i = -3.4 \, \text{cm}\) (inverted, 3.4 cm tall)
Answer: D
-
Critical angle: \(i_c = \arcsin\left(\frac{1.5}{1.6}\right) \approx 70^\circ\)
For total internal reflection: \(i > 70^\circ\)
Relationship with axis angle: \(\alpha = 90^\circ - i\)
\(\alpha < 90^\circ - 70^\circ = 20^\circ\)
Answer: C
-
Plane mirror images are virtual, upright, and same size as the object.
Answer: C
