A 5.0 kg block is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a string that makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal. If the tension in the string is 20 N, what is the acceleration of the block?
A) 1.73 m/s²
B) 2.00 m/s²
C) 3.46 m/s²
D) 4.00 m/s²
E) 5.77 m/s²
Two blocks are connected by a massless string over a frictionless pulley as shown. Block A has mass 4.0 kg and block B has mass 6.0 kg. What is the acceleration of the system?
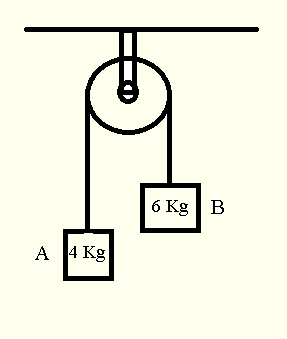
A) 1.96 m/s²
B) 2.94 m/s²
C) 3.92 m/s²
D) 4.90 m/s²
E) 5.88 m/s²
A 2.0 kg block slides down a 30° incline with constant velocity. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline?
A) 0.29
B) 0.50
C) 0.58
D) 0.71
E) 0.87
A car of mass 1200 kg travels around a flat curve of radius 50 m at 15 m/s. What minimum coefficient of static friction is needed to prevent skidding?
A) 0.23
B) 0.35
C) 0.46
D) 0.58
E) 0.69
A 10 kg block rests on a horizontal surface with μₛ = 0.5 and μₖ = 0.3. A force of 40 N is applied at 40° above the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the block?
A) 0 m/s²
B) 1.23 m/s²
C) 1.64 m/s²
D) 2.05 m/s²
E) 2.46 m/s²